Interpretation of the IMDG Code – Deep Analysis of Packaging Construction and Coding System
I. Core Structure of Packaging Codes
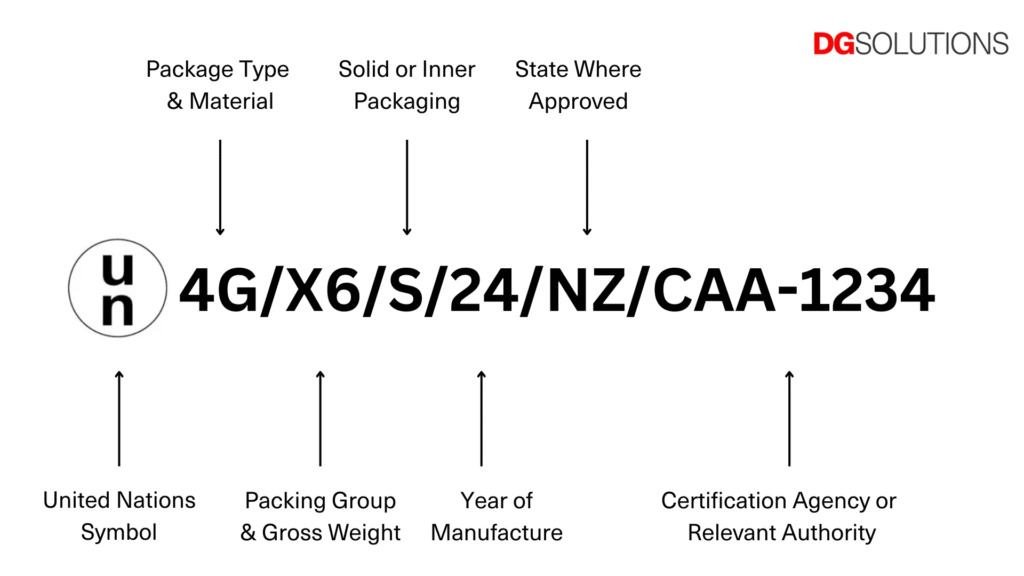
According to IMDG Code Chapter 6.1, UN packaging codes consist of 6 key segments, each representing specific regulatory information:
Example Code: 1A1/Y1.8/150/23/USA/SL123
Packaging Type Identifier (first 2-3 characters)
Number: Packaging form (e.g., 1=drum, 4=box)
Letter: Material type (e.g., A=steel, H=plastic)
Common combinations:
1A1: Closed-head steel drum
4G: Fiberboard box
6HA1: Composite plastic container
Performance Level (Y/Z designation)
Y: Suitable for PG II and III dangerous goods
Z: Only for PG III dangerous goods
*Number**: Relative density requirement (e.g., Y1.8=must withstand liquids with density ≤1.8)
Hydraulic Test Pressure (kPa)
Standard values: 100/150/200 kPa
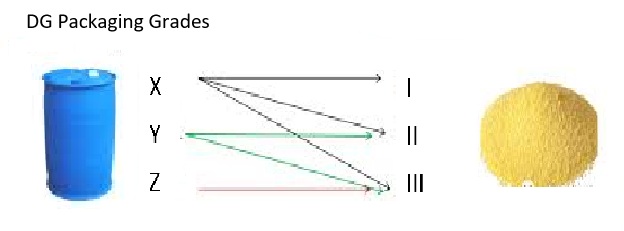
Corresponding packaging groups:
PG I: ≥250 kPa
PG II: ≥100 kPa
PG III: ≥100 kPa
Year of Manufacture
Last two digits (e.g., 23=manufactured in 2023)
*Rule requirement**: Must be retested if over 5 years old
Approving Country Code (ISO two-letter)
USA (United States), CN (China), DE (Germany)
*Special case**: “VL” indicates virtual testing laboratory
Manufacturer Number
Unique identifier issued by national authority
Chinese format: Province code + serial number (e.g., BJ001)
II. Special Packaging Construction Requirements
1. Composite Packaging (6HA1 Series)
Structure: Plastic inner vessel + steel outer frame
Testing requirements:
Inner vessel must pass leakproofness test
Outer frame must pass stacking test (≥3-meter stacking pressure)
2. Salvage Packaging (“S” Designation)
Code example: 1A1/S
Usage restrictions:
For use as secondary packaging only
Capacity must not exceed 50% of original packaging
3. Equivalent Packaging (“E” Designation)
Code example: 1A1/E
Approval process:
Must submit equivalence proof to IMO
Annual certification list updates required

III. Key 2024 Regulation Changes
Mandatory Digital Labeling
All packaging must have QR codes (linking to full test reports)
QR code content must include:
Testing agency certification number
Latest inspection date
Enhanced Requirements for Recycled Plastic Packaging
If recycled plastic content >30%, additional tests required:
UV aging test (500 hours)
Stress cracking test (per ASTM D543)
Lithium Battery Special Packaging (New Class 9)
Code designation: 9A/9B/9C
Special construction:
Short-circuit insulation layer (≥0.1mm)
Pressure relief device (activation pressure ≤50kPa)
IV. Compliance Practice Guide
Packaging Selection Decision Tree
Confirm dangerous goods class → Determine packaging group (PG I/II/III)
Check liquid density → Match Y-value (e.g., density 1.5 requires Y1.8 or higher)
Evaluate transport environment → Select protection type (rust-proof/anti-static/light-proof)
Common Compliance Violations
Error 1: Using PG III packaging for PG II goods (missing Y/Z designation check)
Error 2: Cross-border transport without verifying country approval reciprocity (e.g., CN mark requires re-certification in EU)
Error 3: Using expired packaging without retesting (≥5 years requires retest)
V. Additional Resources
UN Packaging Database: www.unece.org/trans/danger/danger.html
China Certification & Inspection Group: www.ccic.com/packaging-cert
Expert Consultation: Contact Dangerous Goods Packaging Experts
📌 Operation Tip: Always verify packaging code compatibility with dangerous goods list (refer to IMDG Code 4.1.4) before shipment